
English | Malaysia
markets Malaysia
Electricity tariffs for commercial & industrial segment has been increasing around 4% (annualized) since 2006, pushing up costs for businesses. Solar power can help you hedge against this inflation and give you an edge over your competitions. Reach out to us to find out more about our Zero Capex solution.
Malaysia’s Energy Sector Overview
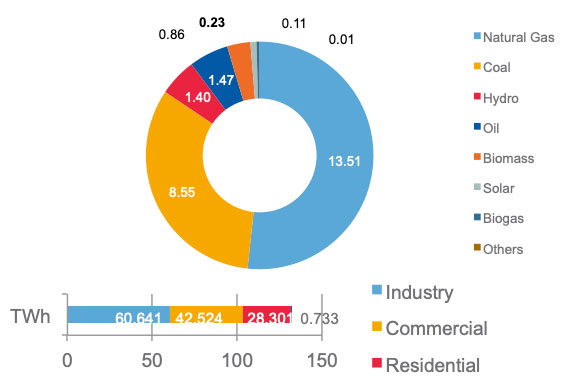
Installed Power Capacity
- Electricity demand growth forecast: 4 – 5%
- Electrification rate : 98.22% (2014)
- Interconnection with Singapore and Thailand, electricity trade is limited to 75GWh of imports and 45GWh of exports.
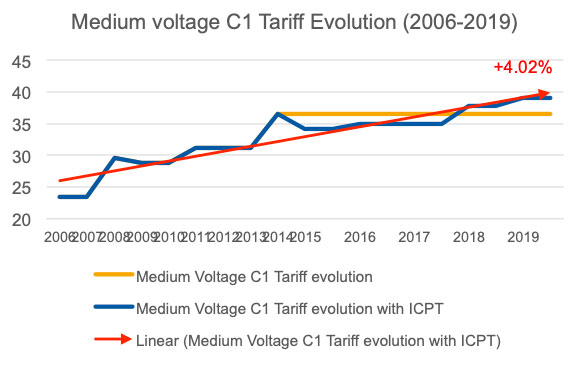
Electricity Prices, Commercial Users
C1 tariff is 0.365 + 1.6% RE Fund + ICPT (2.55 sen)
- 0.396 MYR/kWh landed cost
- Imbalance Cost Pass -Through (ICPT) mechanism allows for TNB to reflect changes in fuel and other generation-related costs in the electricity tariff
Regulation
Government Lead Initiatives:
- Renewable Energy Sources targets: Achieving 20% of Renewable Energy (RE) capacity mix by 2025 (excluding large hydro)
- Carbon reduction target: reduce GHG by 35% by 2030
Implementation
- Net-metering category has been divided into 4 categories which are Residential, Commercial, Industrial and Agriculturefocused on businesses, to target 500 MW through 2020. Excess solar PV generated energy exported back to the grid on a “one-on-one” offset basis from Jan 2019 onwards.
- As subsidies on fossil fuels are scaled back, increasing power prices will benefit solar generation
Project Reference

Carros Center is Singapore’s largest automobile hub.
The PV solar system installation is part of Carros Center’s sustainability efforts to reduce carbon emissions and support Singapore’s effort in mitigating climate change. The project will allow Carros to save around 300 tons of CO2 per year.
View more

TotalEnergies Lubricants is 100% owned by the TotalEnergies Group.
As part of the Group’s commitment to better energy, TotalEnergies is solarizing its own facilities. More than 5000 petrostations have been solarized worldwide.
View more
